The M241D had been designed to be a direct swap for your traditional hot stamp coder with everything you need to install the coder in the box. For more information on how to install your M241D, please refer to the ‘Installing M241D coder' video or Sign In (or Register first, if you haven't already) and then view/download the step-by-step Installation Guide from our Document Library.
The M241D has been designed around digital coding technology. Digital coding is most commonly known as thermal transfer coding and is used for printing onto flexible packaging, as used in Vertical Form Fill and Seal machines, or printing onto self-adhesive labels. The benefits of digital coding compared to traditional host stamp coding can be read in the ‘what is digital coding?’ or ‘product specification’.
Thermal transfer-coding (digital coding) is fundamentally different in operation to a traditional hot stamp coder. The key differences and things to look out for are described below:
Printing Movement:
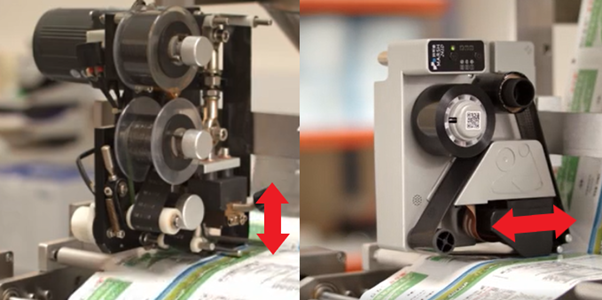
A traditional hot stamp prints by forcing a heated type block (with fixed data) verticle down onto the packaging material, sandwiching ink cover ribbon between. The heated type block melts ink on the ribbon and forces on onto the packaging material – melting and deforming the material surface. This process can be very inconsistent with high print force damaging the print platen and leading to poor print quality and punctured packaging.
The M241D uses a digital printhead to transfer variable data on to the packaging material. Like the traditional hot stamp, the M241D printhead must touch the packaging material and sandwich the ribbon between to transfer a print. However, the M241D requires much less force to do this, causing no damage to the packaging material. To transfer the variable data, once the printhead is touching the packaging material, the printhead is dragged across the material for the length of the required image. At this point, the printhead is withdrawn and returns to the start position as the host machine moves the packaging material ready for the next print.
Things to look out for:
- As stated above, like the traditional hot-stamp, the M241D transfer an image via contact printing. To get the best print quality for the M241D when printing – the packaging material must be stationary when the printhead is in contact with the packaging material.
Please see ‘What is print delay’ and ‘Using print delay – Best practice’ for more information on how the M241D features can help assist the host packaging machine with this.
- The M241D is supplied with a gap setting tool to assist the installation of the coder. This tool ensures the M241D is installed at the correct platen gap to ensure the coder is set at the correct height of optimum print performance. The platen gap tool should be used at any time the M241D coder is moved between machines or knocked during operation.
Please see ‘how do I set the correct platen gap?’ for more information on platen gap. Also, see installation information (stated above) for using the gap setting tool.
- As stated above, like the traditional hot-stamp, the M241D transfer an image via contact printing. The printheads traverse across the print platen to transfer the image. If the platen rubber is damaged or worn – this will be mirrored in the printed image. Damaged or worn platen rubber will cause print defects in the transferred image. If your M241D print quality degrades – check the print platen has not become damaged.
Printhead Technology:

Traditional hot-stamp coders use brass type blocks that hold fixed data characters (numbers, letters or symbols). The type block is heated and pressed onto the packaging material, melting the ribbon and deforming the packaging material at the same time.
The M241D uses a digital printhead to transfer variable data to the packaging material. The edge of the digital printhead that contacts the ribbon and packaging material has a series of electrical resistors (dots) which are heated on command by the M241D software. As the printhead is dragged across the packaging material, the software turns on/off the relevant dot to melt the specific point on the ribbon to create an image. The resistors (dots) are covered in a protective layer of ceramic to ensure a long run life.
Things to look out for:
- The printhead is an electrical component and like all electrical components, it does work well when it comes in contact with other metal surfaces. Ensure the M241D platen does not have any metal obstruction which the printhead could contact.
- The printhead is to be low maintenance consumable compared to traditional hot-stamp type blocks. However, the ceramic coating that protects the resistors (dots) can become coated in ribbon ink over time. This prevents the resistors from working optimally and can cause the print quality of the M241D to degrade.
Please see ‘Printhead Care’ and ‘How do I clean the printhead’ articles for more information on the digital printhead and maintenance.

